In quandary over how to become a software tester?
Over the years, the demand and market size for software testing has been steadily blooming.
And rightly so! In this day and age of smartphones and smart everything, applications and software have become a crucial part of our everyday lives.
In 2019 alone, the market size of software testing surpassed $40 billion and is anticipated to grow at a rate of 6% by 2026.
So what does a software tester primarily do?
A software tester is responsible for ensuring that new software and applications comply with the expected standard and the intended purpose.
They are part of the quality assurance team and work to make sure that the software products or applications are error-free and user-friendly.
Since testing is a critical part of the product life cycle, testers usually become a part of every stage in the software development process, especially in the later stages.
Also, understanding the purpose and goal of the software is extremely important for software testers because how else would they identify software faults and bugs?
An ideal candidate for the role of a software tester has to have a keen eye for details, errors, and areas of improvement, along with a basic knowledge of coding and programming languages.
Here’s what this blog will be covering:
- What qualifications do you need to be a software tester?
- How to become a software tester without a degree?
- What is the best software tester certification?
- What are the software skills and technical skills required for software tester?
- What are some of the alternate career options for a software tester?
- What is a software tester salary?
How to Become a Software Tester?
In a usual scenario, an aspiring software tester begins his/her journey by ensuring that they have the necessary qualifications that are required to become a software tester.
Most software testers have an educational background in computer science, electrical engineering, computer information systems, and business management.
According to Zippia.com, the most common colleges opted by aspiring software testers in the US are:

Best Colleges to Get a Degree for Becoming a Software Tester
As stated earlier, there is no standard degree that is required to become a software tester.
However, it is necessary to major in a subject that is related to software testing.
Best Colleges for Computer Science & Electrical Engineering Degree
| COLLEGE | TUITION FEES |
|---|---|
| Carnegie Mellon University | $800/credit |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | $77,020/year |
| Cornell University | $30,143/semester |
| University of California (Berkeley) | $5,721/semester + $14,877 (out of state) |
| University of Illinois (Urbana-Champaign) | $8,674/semester + $17,399 (out of state) |
| University of Washington | $12,076/year (in state); $39,906/year (out of state) |
| Georgia Institute of Technology | $5,129/semester (in state); $15,685 (out of state) |
To learn more about the job profile of a software tester, you can read:
How to Become a Software Tester Without a Degree?
If you are someone who is looking to make a career switch and aspiring to become a software tester without a degree in computer science, yes, it is possible to do so.
Although some recruiters have strict guidelines for education requirements while hiring a software tester, many recruiters are willing to excuse the lack of a degree in computer science.
That is, if you have the right certification, training, or some sort of experience in the IT service industry.
Best Software Testing Certification
Consider taking up any one or a combination of the listed certifications to pursue a career in software testing.
These certifications are also helpful for candidates who are wondering how to become a software tester with no experience in testing but have experience in working in the IT industry.
- CAST (Certified Associate in Software Testing)
- CSQA (Certified Software Quality Analyst Certification)
- ISTQB Certification (International Software Testing Qualifications Board)
- CQE (Certified Quality Engineer)
- CMST (Certified Manager of Software Testing)
- CSTE Certification (Certified Software Tester)
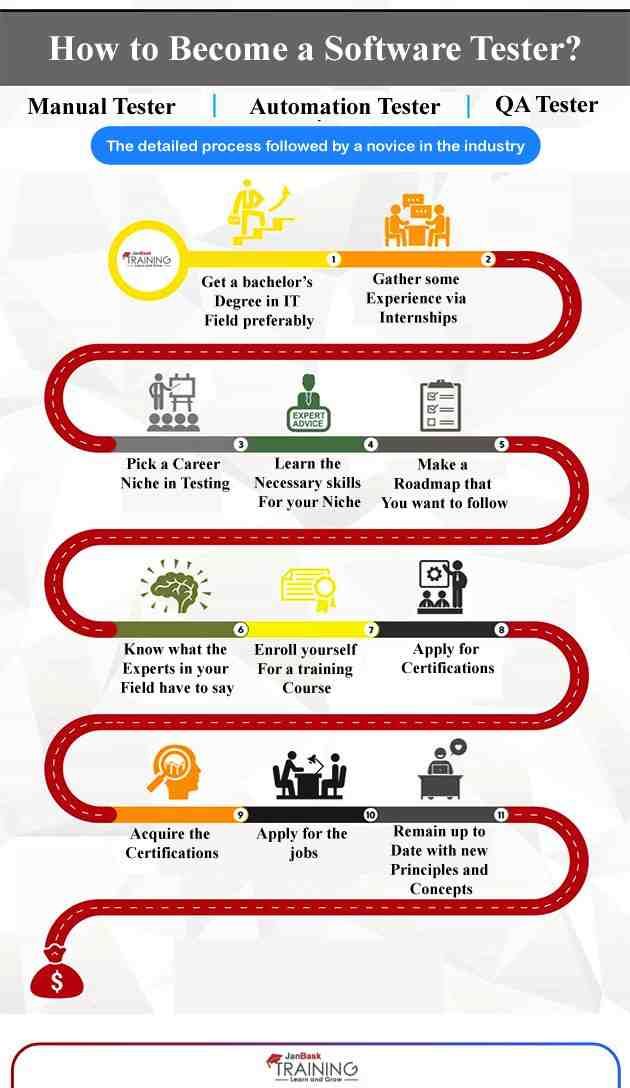
Source: JanBask
Software Skills and Technical Skills Required for Software Tester
When it comes to becoming a software tester, the entire point of acquiring a degree, and getting certified is to hone your software skills and testing abilities.
Take a look at the must-have key skills to become a software tester:

Technical Skills
Since the job profile of a software tester is a technical one, it also demands the candidate to possess competence in various techniques and familiarity with software tools such as:
- SDLC (software development life cycle)
- STLC (software testing life cycle)
- Linux commands & basic programming
- Design & IDE tools like Rational Rose, WebLogic Server
- Selenium
- TestingWhiz
- Testim
- Kobiton and so on
Alternate Career Options for a Software Tester
After gaining experience as a software tester, you can also consider making a career switch to various other job profiles that require similar educational backgrounds and skills.
The following are some of the career tracks that you can choose after becoming a software tester:
Automation Tester
An automation testing engineer is responsible for conducting software tests by using various automated software tools to ensure that the end product meets all the specifications without any errors.
Automation testers usually write in C#, JavaScript, and Ruby programming languages and use tools like IBM Rational Robot, Silk performer, and QTP.
Also, these professionals need to be adept at ATLC (Automation Testing Life Cycle) methodologies to facilitate a robust and stable automation framework.
Performance Tester
The chief responsibility of a performance tester is to check the new application's responsiveness, including the time it takes to load, the maximum load that the application can handle, and so on.
They assess the software or application's scalability, resource usage, stability, and reliability to ensure that the product meets the quality standards before it reaches the end-users.
Given below are the 6 types of performance testing conducted by performance testers:
- Load Testing
- Stress Testing
- Endurance Testing
- Spike testing
- Volume testing and
- Scalability testing
Business Analyst
One of the advantages software testers have over software developers is that they have a good range of business knowledge due to the nature of their work.
And as a software tester, if you figure out that you enjoy focusing on organizational aspects, you could switch your career to business analyst.
As a business analyst, you will be responsible for analyzing data to identify important patterns and information that are crucial for business growth and development.
Software Tester Salaries
In the US, the software tester salary on average centers around $56,448 per annum.
This figure changes according to the candidate’s experience level, skills, location, industry, and company.
| EXPERIENCE LEVEL | SALARY |
|---|---|
| Fresher | $48,548 |
| Mid Career | $68,533 |
| Senior | $80,924 |
Meanwhile, the following cities in the US are among some of the highest paying locations for software tester jobs:
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Austin, TX
- Chicago, IL
- Los Angeles, CA
Now that you have a clear understanding of how to become a software tester, start preparing to apply for software tester jobs with a notable software tester resume and a cover letter!
Takeaways from the Blog
- A software tester is responsible for ensuring that new software and applications comply with the expected standard and the intended purpose
- A software tester runs manual and automated tests to identify bugs and areas of improvement
- An ideal candidate for the role of a software tester has to have a keen eye for details, along with a basic knowledge of coding and programming languages
- Most software testers have an education background in computer science, electrical engineering, computer information systems, and business management
- If you have the right certification, training, and experience in working in an IT service industry, you can become a software tester without a degree in computer science
- CAST, CSQA, CQE, and CMST are some of the most popular software testing certifications among others
- Aspiring software testers must be familiar with using software testing tools such as Selenium, TestingWhiz, Testim, Kobiton, and so on
- Good analytical, communication and programming skills add value to your candidacy as a software tester
- The average software tester salary of a professional working in the US is $56,448 per annum
Need more career-related assistance? Visit our career platform with 24x7 chat support and write to us at support@hiration.com. Happy to be of service!



