How to start or switch to a career in manufacturing?
Explore in-demand roles, pick a target path, and secure the needed vocational training, apprenticeship, or degree. Build technical and soft skills, tailor your resume and search strategically, and leverage transferable strengths if changing fields.
The U.S. manufacturing sector is facing a seismic shift.
Over the next decade, 3.8 million jobs will need to be filled, yet more than half could remain vacant due to a widening skills gap, according to a report by Deloitte and The Manufacturing Institute.
So, if you’re considering this industry, there has never been a better time to get started, or to level up your existing skills.
Whether you’re starting your career or making a switch, manufacturing rewards those who can adapt, innovate, and learn.
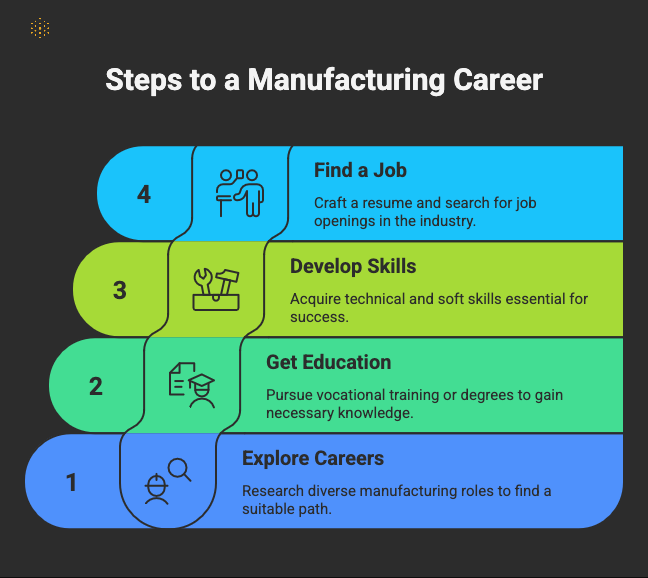
This guide will walk you through 4 key steps to help you break into, or advance within, one of the most vital and dynamic industries in the world.
Step 1: Explore In-Demand Manufacturing Careers
The first step is to explore the diverse career paths available in the manufacturing industry. Here are some of the most in-demand roles:
- Industrial Production Managers: These professionals oversee the daily operations of manufacturing plants. They ensure that production is efficient, on schedule, and within budget. This role typically requires a bachelor's degree and several years of experience in a related field.
- Engineers: Engineers are the true problem-solvers of the manufacturing world, each bringing their own specialty to keep things moving efficiently. Mechanical Engineers dream up, design, and test everything from intricate tools to massive engines and machines. Industrial engineers take a big-picture view, streamlining processes and systems to cut out waste and make production smoother. Meanwhile, process engineers dive deep into the details of manufacturing, fine-tuning operations to boost efficiency and bring down costs. Together, they turn ideas into practical, efficient realities.
- Quality Control Inspectors: These individuals are responsible for ensuring that products meet a set of predetermined quality standards. They inspect, test, and measure materials or products being produced.
- Machinists and CNC Programmers: Machinists set up and operate a variety of machine tools to produce precision parts and instruments. Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) programmers write the code that automates these machines.
- Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers: These skilled tradespeople use hand-held or remotely controlled equipment to join or cut metal parts. They are essential in many manufacturing sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.

Step 2: Get the Right Education and Training
Once you have an idea of the career path you want to pursue, the next step is to get the right education and training. The educational requirements for manufacturing jobs vary widely.
- Vocational Training and Apprenticeships: Many skilled trades, such as welding and machining, can be entered through vocational training programs or apprenticeships. These programs offer hands-on training and are a great way to enter the workforce quickly.
- Associate's and Bachelor's Degrees: For more technical and managerial roles, such as engineering or supply chain management, a two- or four-year degree is often required. A degree in a field like mechanical engineering, industrial engineering, or supply chain management will provide you with a strong foundation for a successful career.
Step 3: Develop Essential Skills
To succeed in the manufacturing industry, you'll need a combination of technical and soft skills.
Technical Skills
- Machining and Fabrication: The ability to operate and maintain manufacturing equipment is a core skill.
- Welding and Joining: Essential for many roles in the automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors.
- Quality Control: Understanding how to inspect products and ensure they meet quality standards is crucial.
- CNC Programming: With the rise of automation, the ability to program CNC machines is a highly sought-after skill.
- Lean Manufacturing: Knowledge of lean manufacturing principles helps to minimize waste and maximize productivity.
Soft Skills
- Problem-Solving: Manufacturing professionals are constantly faced with challenges, so the ability to think critically and find solutions is essential.
- Teamwork: Most manufacturing jobs require you to work as part of a team, so strong collaboration and communication skills are a must.
- Adaptability: The manufacturing industry is constantly changing, so the ability to adapt to new technologies and processes is vital for long-term success.
- Attention to Detail: Precision is key in manufacturing. A keen eye for detail ensures that every component and product meets the required specifications.
Step 4: Craft a Winning Resume and Find a Job
With the right education and skills, it's time to find a job.
- Write a Compelling Resume: Your resume is your first impression, so make it count. Tailor it to each job application, highlighting the skills and experience that are most relevant to the position.
- Search for Job Openings: Look for job openings on online job boards, company websites, and professional networking sites like LinkedIn. You can also work with recruiters who specialize in the manufacturing industry.
- Prepare for Interviews: Practice answering common interview questions and be prepared to discuss your skills and experience in detail. Use concrete examples to demonstrate your problem-solving abilities, attention to detail, and leadership skills.
A Note for Career Changers
It's never too late to switch to a career in manufacturing. The industry values experience from all backgrounds, and many of your existing skills are likely transferable.
- Highlight Transferable Skills: Skills like project management, data analysis, problem-solving, and team leadership are highly valued in manufacturing. When updating your resume, be sure to showcase how your previous experience has prepared you for a role in this new field. For instance, if you have a background in data analysis, you can emphasize how those skills can be applied to optimize production metrics and quality reports.
- Focus on Adaptability and Willingness to Learn: The manufacturing landscape is constantly evolving. Emphasize your ability to learn new technologies and processes quickly. Your adaptability and fresh perspective can be a significant asset to a manufacturing team.
- Seek Out "Bridge" Opportunities: Look for roles that can serve as a bridge between your old career and your new one. For example, if you have a background in IT, you could look for a role in a manufacturing company's IT department to get your foot in the door. From there, you can learn more about the industry and potentially transition into a more production-focused role. Companies often invest in training and upskilling their employees, allowing them to develop new skills and advance their careers.
Conclusion
A career in manufacturing offers a stable and rewarding path for individuals with a wide range of skills and interests.
And if you want to make that leap with confidence, Hiration can help you create an ATS-friendly resume, sharpen your interview skills, and optimize your LinkedIn profile.
The opportunities are out there - it’s up to you to take the first step!
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the 4 steps to start or switch to a career in manufacturing?
Follow 4 steps: Explore in-demand manufacturing careers; get the right education and training; develop essential skills; craft a winning resume and find a job.
-
What manufacturing roles are in demand?
Pursue roles such as Industrial Production Managers, Engineers, Quality Control Inspectors, Machinists and CNC Programmers, and Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers.
-
Do you need a degree to work in manufacturing?
It depends on the role. Many skilled trades can be entered through vocational training or apprenticeships, while more technical and managerial roles often require a two- or four-year degree.
-
What technical skills do manufacturing employers look for?
Key technical skills include Machining and Fabrication, Welding and Joining, Quality Control, CNC Programming, and Lean Manufacturing.
-
What soft skills help you succeed in manufacturing?
Emphasize Problem-Solving, Teamwork, Adaptability, and Attention to Detail.
-
How should you tailor a manufacturing resume?
Tailor it to each job application, highlighting the skills and experience most relevant to the position. Your resume is your first impression, so make it count.
-
How can you prepare for a manufacturing job interview?
Practice answering common interview questions and prepare to discuss your skills and experience in detail. Use concrete examples to demonstrate problem-solving, attention to detail, and leadership.
-
Is it too late to switch to a manufacturing career?
It's never too late to switch to a career in manufacturing. The industry values experience from all backgrounds, and many of your existing skills are likely transferable.
-
What is the difference between machinists and CNC programmers?
Machinists set up and operate a variety of machine tools to produce precision parts and instruments. CNC programmers write the code that automates these machines.
-
What does an Industrial Production Manager do?
They oversee the daily operations of manufacturing plants and ensure production is efficient, on schedule, and within budget. This role typically requires a bachelor's degree and several years of experience.



