How can career centers build goal-setting worksheets that work in a skills-first hiring market?
Career centers need to move beyond task-based SMART goals and design worksheets that prioritize skill evidence, adaptability, and follow-through. In a market where employers screen for competencies rather than activity volume, effective goal-setting tools help students identify target skills, document proof of use, address gaps early, and translate academic work into employer-ready outcomes.
If you work in career services, you’ve almost certainly used the SMART framework - Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound to help students set goals.
Although this framework turns “I want a job” into “I’ll apply to three marketing internships by Friday", in a skills-first hiring market, that clarity often stops at activity.
Students complete tasks, while employers and automated screening systems look for proof of competency.
When 52% of employers now relax degree requirements in favor of skills, static goals start working against students.
Counting applications or deadlines met doesn’t answer the question that determines visibility and hiring: what skill did the student demonstrate, and where is the evidence?
To close that gap, career centers need goal-setting tools that shift from task tracking to evidence-building.
Here’s a breakdown of how you can move goal-setting worksheets beyond SMART so they drive career agility, competency evidence, and follow-through in a skills-driven, AI-influenced job market.
Why should CSPs move beyond SMART goals in 2026?
Modern career coaching must pivot to Career Agility to help students survive a volatile market where skills, not just titles, are the primary currency. Because 9.7% of new graduates faced unemployment in late 2025 according to NACE. Students need worksheets that prioritize evidence-building over simple task completion to remain competitive.
Standard SMART goals fail to address "application inflation."
According to the 2025 NACE Student Survey, students now submit a median of 10 applications compared to just 6 in 2024.
If a student's only goal is the number of applications, they ignore the quality of their skill-mapping.
Your worksheet must shift focus to "Competency Goals." Here's how to adapt your coaching:
- The "S" is for Skill, not just Specificity: Instead of "Apply to X," the goal should be "Demonstrate Analytical Thinking by completing X."
- The "A" is for Agile, not just Achievable: Create "Pivot Plans." If the primary industry (e.g., tech) freezes hiring, what is the secondary skill-adjacent industry (e.g., data analytics in healthcare)?
Also Read: How to boost student attendance at career fairs?
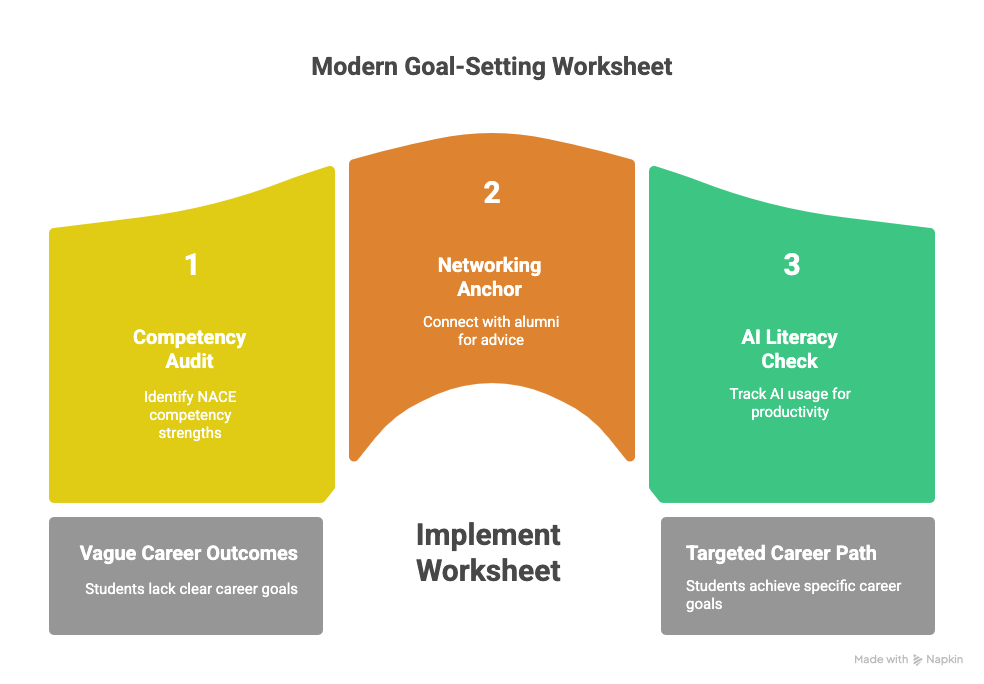
What specific sections must a modern goal-setting worksheet include?
A high-impact 2026 worksheet must include a Competency Audit, a Networking Anchor, and an AI Literacy Check. This moves students away from vague outcomes and toward identifying the 8 NACE competencies like Critical Thinking or Equity & Inclusion.
According to LinkedIn’s 2025 Workplace Learning Report, professionals using AI-powered training to practice skills saw an 83% increase in confidence. The worksheet should explicitly track how a student uses AI for productivity, such as keyword optimization or interview simulation.
Essential Worksheet Components:
- The Evidence Log: Space for the student to write one "STAR" story (Situation, Task, Action, Result) for a specific NACE competency each month.
- The "Human" Anchor: A requirement to list one person, not a job board they will speak to. This fights the "black hole" of online applications.
- The Skill-Gap Box: A section where the student lists one skill they see in job descriptions that they don't have yet, and a 30-day plan to learn it.
Here's a career agility worksheet sample:
Part 1: The Competency Spotlight
Don't just list what you did; list what you proved. Pick one NACE Competency (e.g., Communication, Technology, Leadership).
- Target Competency: __________________________________
- Monthly Evidence Goal: "By the end of this month, I will have a specific example of using this skill in my [Club/Class/Job]."
- Verification: Who can vouch for this skill? (Name a Professor/Supervisor): _________________
Part 2: The Skill-Gap Audit (Skills-Based Hiring Prep)
52% of employers prioritize skills over degrees. Find a job posting you like and audit it.
- Top 3 Skills Requested: 1. _________ 2. _________ 3. _________
- The Gap: Which one am I weakest in? ___________________
- Agile Action: I will spend 2 hours this week on [LinkedIn Learning/Coursera/Project] to learn the basics of this skill.
Part 3: AI & Efficiency Check
- AI Tool of the Week: (e.g., "Using ChatGPT to mock-interview me for X role") _________________
- Prompt/Result: What was one helpful thing the AI suggested for your resume? _________________
Part 4: The Networking Anchor
- The "Human" Goal: I will reach out to one Alum at [Company Name] for a 15-minute "Prototyping Conversation."
- Status: [ ] Drafted message [ ] Sent [ ] Meeting Scheduled
Also Read: How can career centers close the equity gap for FGLI students?
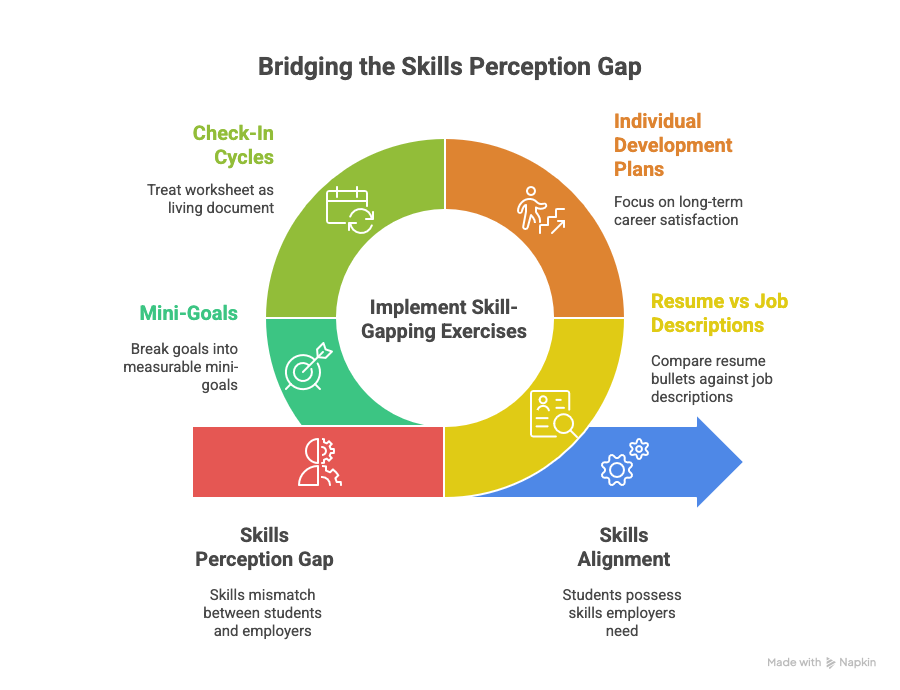
How can we bridge the "perception gap" between student skills and employer needs?
CSPs must also use worksheets to facilitate "Skill-Gapping" exercises that force students to compare their current resume bullets against real-world job descriptions. This is vital because 92% of hiring professionals say soft skills are as important as hard skills, according to WeCP's 2026 Trends.
Universities like the University of Iowa have implemented "Individual Development Plans" (IDPs) that move beyond task-completion to focus on "long-term career satisfaction" and university-wide alignment.
This approach helps students articulate why their goals matter, which is the missing link in most basic worksheets.
Also Read: How to guide international students through interviews?
How can you ensure students actually follow through on these worksheets?
Implementation requires moving from "One-and-Done" sessions to "Check-In" cycles where the worksheet is treated as a living document. Integrating these into first-year experience (FYE) programs - as 57% of schools currently do, ensures students are building evidence early rather than scrambling in their senior year.
Colleges like Purdue Global emphasize breaking attainable goals into "mini-goals" that are measurable, allowing students to monitor progress and adjust strategies as market conditions change.
By focusing on what they can control, their environment and their skill acquisition - you can empower them to handle the 2026 job market's complexity.
Also Read: How can career centers prepare students for AI-driven interviews?
To Sum Up
Redesigning goal-setting worksheets around skills, evidence, and adaptability only works if students can keep building momentum after the appointment ends.
Otherwise, even the best framework fades once the worksheet goes back into a folder.
If you’re looking for tools that reinforce this kind of growth beyond the workshop, from exploration and job matching to polished application materials and interview practice, Hiration brings those elements together in one place.
It gives students round-the-clock support while giving counselors a clearer, more streamlined way to guide cohorts and see progress over time.
The real shift isn’t replacing advising with technology.
It’s using the right tools to extend your impact - so every goal a student sets turns into visible skill evidence, not just another box checked.
Skills-First Goal-Setting Worksheet FAQs
Why are SMART goals no longer enough for students?
SMART goals focus on task completion, not skill demonstration. In a skills-first hiring market, completing applications does not show employers what a student can actually do or where that skill is evidenced.
What should replace task-based goals in career coaching worksheets?
Worksheets should shift toward competency goals that require students to identify a skill, build evidence of using it, and document outcomes that align with employer expectations.
What core sections should a modern goal-setting worksheet include?
A modern worksheet should include a competency audit, an evidence log tied to NACE competencies, a skill-gap assessment, a networking anchor, and a structured way to track AI-assisted skill development.
How does a skills-first worksheet help reduce application inflation?
By shifting attention from volume to quality, students focus on improving skill alignment and proof rather than submitting more applications without improving competitiveness.
How can worksheets help students translate academic work into employer language?
Worksheets can prompt students to rewrite academic experiences using outcome-based, employer-facing language that highlights transferable skills instead of coursework or titles.
How can career centers improve student follow-through on goal-setting?
Treat worksheets as living documents with regular check-ins rather than one-time exercises. Embedding them into first-year experience programs helps students build evidence consistently over time.
Why is adaptability critical in goal-setting for the 2026 job market?
Hiring conditions change quickly. Worksheets that include pivot plans and skill-adjacent pathways help students respond to market shifts without restarting their search from scratch.



